3D Metrology Services – Tool & Die – Form Inspection & Comparison to CAD
At EDM Intelligent Solutions, our high-resolution 3D scans of piece parts allow for form measurement down to the µm scale. A form measurement is made by cutting profiles across the 3D part scan data set and those included points are used to gather various form dimensions including radii, angles, slot width, height step and more.
Our 3D Metrology solutions utilize automated comparisons of high-resolution 3D part scans against the original CAD model, as well as additional 3D scanning services for quick and accurate difference measurements. 3D scans of the piece part containing millions of data points are compared to ideal CAD models to verify dimensional accuracy of the entire part, or a specific feature. With our 3D Metrology Services, we’re able to offer our customers in-depth, non-contact measurements of almost any shape, size, and form.
Below is an example of a difference measurement and a form inspection of a miniature lens housing. This is a four step process. The difference evaluation, form inspection, and 3D measurements of this component were completed using our MVi5 3D Metrology Center.
APPLICATION DETAILS
- Component – Precision Die Insert
- Material – Hardened Tool Steel
- Metrology Services:
- Difference Measurement
- Form Inspection
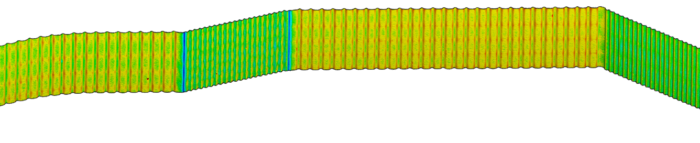
Step1: Capture 4mm Wide Scan

Step 2: 3D Comparison to CAD
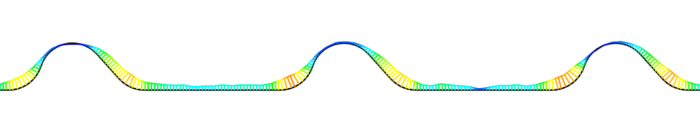
Step 3: Profile Comparison to CAD
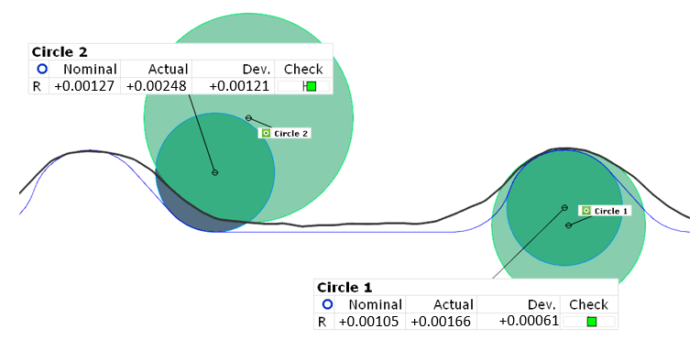
Step 4: Extract Measurements
COMPETITIVE 3D METROLOGY, MEASUREMENT, AND INSPECTION SERVICES
Intelligent solutions to manufacturing and measurement challenges are what we do. Over the past 25 years, we’ve completed thousands of measurement and metrology projects. What differentiates EDM Intelligent Solutions 3D Metrology services from the competition is our unique understanding of each manufacturing process. The EDMIS metrology technicians and applications engineers support their colleagues in our tight tolerance CNC machine shop that produces ultra-precision components for customers every day. Harnessing this unique relationship with manufacturing, our metrology team has the experience needed to fully assist our customers leverage the measurements taken of their components to improve their manufacturing processes. We are confident that we can measure your most challenging components and work with you to fully understand what those measurements tell you about them. To learn more about how EDMIS can help you, contact our metrology team with your request for quote.